Did you know over 15,000 substances can cause allergic skin reactions? This shows how crucial patch testing is for pinpointing what makes skin react. It’s vital for people with skin allergies. This test figures out what bothers your skin. This way, skin doctors can create a plan that works for you.
Patch testing is a major tool in dermatology. It can find around 80% of what causes skin issues, which is super helpful for people with jobs exposing them to unique allergens. Think of florists or dentists. It’s key in treating different types of contact dermatitis, making life better for many.
Getting a patch test helps in two ways. It finds out what causes your skin to flare up and teaches you how to avoid these things. By getting tested, you’re doing something important for your skin’s health. It helps you stay away from what irritates your skin.
Key Takeaways
- Over 15,000 substances can cause allergic skin reactions.
- Patch testing identifies about 80% of allergens, aiding in effective management.
- Irritant contact dermatitis accounts for approximately 80% of cases.
- Many professionals, such as florists, are at higher risk for job-specific allergies.
- Nickel sulfate is the most common allergen detected, particularly in body piercings.
Understanding Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a common skin problem caused by touching irritants or allergens. It comes mainly in two types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis (ACD). ACD affects many people, making it quite widespread.
Patch testing is a key way to find what allergens cause ACD. It involves putting small allergen samples on the skin, usually the back, for about 48 hours. Watching for skin reactions during this time helps doctors make a clear diagnosis.
It’s very important to correctly find allergens with patch testing. Knowing what causes your reaction helps you avoid those triggers. This way, you can prevent future issues. Contact dermatitis often isn’t dangerous, but it can really impact your life if not managed well.
Patch tests are crucial for better handling of ACD. They let doctors identify specific triggers like nickel, cosmetic products, and cleaners using a panel of thirty or more items. If patch tests show no reaction, it means those substances aren’t causing your problem. But, sometimes more tests are needed to find the exact cause of your allergies.
What Causes Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis comes from many things outside the body. It splits into two kinds: irritant and allergic. It’s vital to know these to control and stop the condition.
Irritant contact dermatitis is often caused by common things like soaps and cleaners. These things can hurt the skin directly. They make the skin inflamed and itchy, showing up as redness and itchiness.
On the other hand, allergic contact dermatitis happens when skin responds to certain allergens. Examples of these are:
- Nickel
- Fragrances
- Preservatives
- Balsam of Peru
- Formaldehyde
- Cobalt
How likely you are to get allergic contact dermatitis often depends on genes. If exposed to allergens, the immune system might react too strongly. This can cause swelling, blisters, and skin peeling.
Figuring out the exact cause of contact dermatitis helps a lot. Patch tests do this well for about 70% of allergic cases. They help patients and doctors find the right way to deal with allergens.
The Role of Allergens in Contact Dermatitis
Allergens play a big part in starting allergic contact dermatitis. This is when the immune system reacts to certain substances. At first, a person may not show any reaction. But after being sensitized, a repeat exposure can lead to a delayed hypersensitivity reaction. This may cause symptoms ranging from mild irritation to severe ones.
Some common allergens are nickel, found in many types of jewelry, and fragrance mixes used in personal care items. Others include methylchloroisothiazolinone/methylisothiazolinone and para-phenylenediamine. Knowing about these allergens is key. They are involved in starting an inflammatory response marked by redness, swelling, and blistering.
Allergic contact dermatitis makes up about 20% of all contact dermatitis cases. Irritant contact dermatitis forms the other 80%. Between 1.7% and 9.8% of people in general have contact dermatitis. Notably, 15.0% to 20.1% of those tested show allergies to contact. Certain jobs, like hairdressing and healthcare, have a higher risk due to more allergen exposure.
The inflammation in allergic contact dermatitis comes from certain chemicals and T cells reacting after meeting the allergen again. So, finding these allergens with patch testing is vital. Patch testing is not just a fast way to spot the allergens. It’s also crucial for teaching patients how to avoid them.
For more on how patch testing helps diagnose contact dermatitis allergens, visit this resource.
Types of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis has several kinds, each unique in its way. Knowing these kinds is key for the right diagnosis and treatment. We have irritant contact dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, photocontact dermatitis, and contact urticaria.
Irritant contact dermatitis comes from direct skin damage by things like chemicals or soaps. It appears quickly after contact, causing redness, itching, and sometimes blisters. Allergic contact dermatitis, however, is different. It happens when the skin reacts to allergens like nickel or fragrances, causing an immune response.
Photocontact dermatitis is when certain chemicals react under UV light, leading to skin issues. This is common with some sunscreens. Contact urticaria shows up as hives after touching things that release histamine, like certain foods or latex.
Knowing these types helps pick the right treatment and avoid more skin problems. For example, allergic contact dermatitis often affects the hands. In fact, 64 percent of workers with this condition report symptoms on their hands.
Importance of Patch Testing in Contact Dermatitis
Patch testing is key in assessing allergic contact dermatitis. It helps find what substances cause skin issues. Importance of patch testing in contact dermatitis is huge. It lets dermatologists make personal treatment plans. This improves patient comfort and life quality.
How Patch Testing Helps Identify Allergens
The patch testing procedure involves placing allergens on the skin under tape. They stay there for 48 to 72 hours. This process is great at finding delayed skin reactions.
Patients must avoid creams and oral steroids before the test. Doing so ensures the results are accurate. Proper patch tests help doctors find what causes the irritation. Knowing this helps people stay away from those allergens, reducing allergic reactions.
Benefits of Accurate Diagnosis through Patch Testing
Getting a right diagnosis with patch testing has many benefits. It pinpoints allergens that inflame the skin. This knowledge helps people avoid these substances. Avoiding them can lead to healthier skin and more effective skincare.
Those wanting to try new beauty products should do patch testing first. This reduces possible skin problems and saves money. With the right prevention and treatments, people can handle skin issues better. This boosts their quality of life. For more on this topic, see the best tools for diagnosing eczema.
The Patch Testing Procedure
Patch testing is key for figuring out contact dermatitis and what causes it. It helps doctors see how your skin reacts to different things. Knowing what happens during this test can make it less worrisome and easier to go through.
What to Expect During Patch Testing
In patch testing, tiny amounts of allergens are put on your skin and covered. They stay there for 48 hours. This time lets any allergic reactions show up. After 48 hours, you go back to the clinic so doctors can see how your skin reacted. Doing the test right makes sure the results are accurate.
Key Steps in the Patch Testing Process
The patch testing process has important steps for good results:
- Initial Assessment: Doctors look at your health history and guess which things might cause allergies.
- Patch Application: They carefully put patches with allergens on your skin so they’re in the right spot.
- Monitoring: You have to keep the test spot dry. Also, don’t sweat too much or scratch it.
- Patch Removal: After 48 hours, the patches are taken off so doctors can check for reactions.
- Follow-Up Consultation: Talking with your doctor afterwards is important to figure out the next steps.
You shouldn’t use skin creams on the test area for a week before the test. Also, stay out of the sun for 1 to 2 weeks before testing. Following these rules helps you understand more about what your skin is sensitive to.
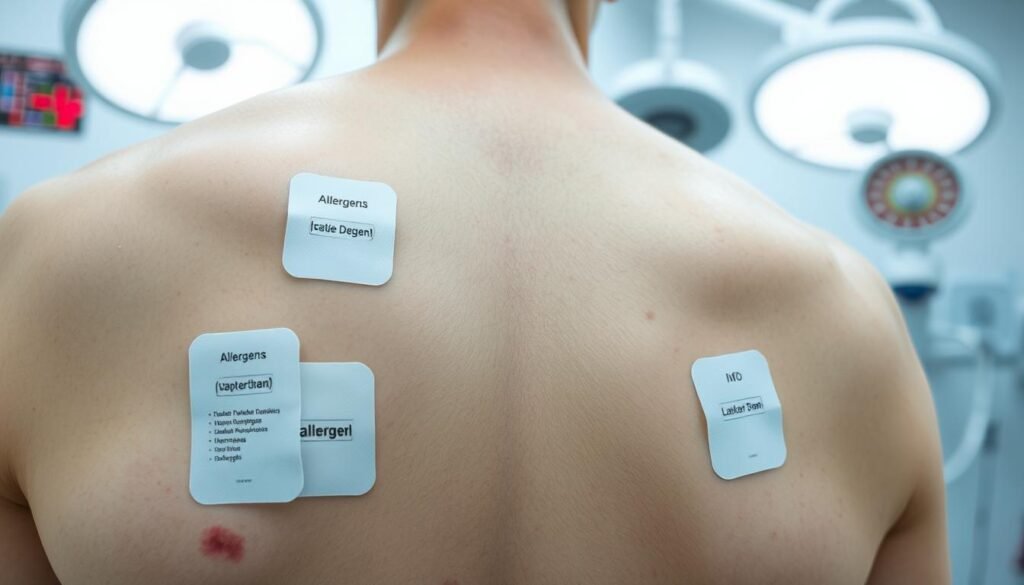
Patch Testing Guidelines and Best Practices
To get accurate results, patch testing guidelines are essential. It’s important to pick the right allergen panels. This choice is based on the patient’s history and exposures. When deciding which allergens to test, dermatologists take into account both personal and work-related factors. This ensures the tests are relevant to the patient’s environment.
The skin needs to be in good shape before starting the tests. Places with fresh wounds or active skin issues might not give true results. Telling patients not to wet or irritate the test area helps patch testing accuracy. This care reduces irritation risks, making sure the reactions are real.
Teaching patients about the patch test is key. Clear guidance about what to expect and following instructions can help avoid wrong results. Better communication means patients know some reactions might show up later. This means reading results more than once is necessary.
| Best Practice | Description |
|---|---|
| Stable Skin Condition | Ensure the skin is free from active dermatitis or surgical wounds prior to testing. |
| Allergen Selection | Choose allergen panels based on individual and occupational exposure history. |
| Patient Preparation | Instruct patients to keep the application site dry and avoid irritants. |
| Follow-up Readings | Conduct readings at appropriate intervals to assess mixed reactions. |
| Education | Provide clear guidelines and support to enhance patient compliance and understanding. |
Using these patch testing guidelines can make diagnosis better. When patients know more, they get more reliable test outcomes. This helps in treating contact dermatitis and similar issues.
Spotting eczema signs early helps in finding the best treatment. Listening to patients and understanding their symptoms betters skin condition management. This leads to improved patient results, as shown in studies about catching symptoms and good skin care.
Interpreting Patch Test Results
Understanding patch test results is key in diagnosing allergic contact dermatitis. Positive reactions point to specific allergen sensitivities. These need careful review. It’s vital to consider the patient’s history to understand these results’ significance over time.
Understanding Positive Patch Test Reactions
Positive reactions from patch tests fall into different severity categories. Recognizing these levels is crucial. This varies from mild irritation to severe symptoms like blistering. Knowing these helps doctors advise patients on avoiding certain allergens.
Grading Reactions in Patch Testing
Standardized methods are used to grade patch test reactions. Typically, these reactions are checked 72 to 96 hours after allergen exposure. This wait helps identify true allergic responses. Below is a table showing common grading systems:
| Grade | Description | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No reaction | No sensitization detected |
| 1+ | Mild erythema | Possible sensitization, needs more evaluation |
| 2+ | Clear vesicles or papules | Sensitization confirmed; avoid certain substances |
| 3+ | Severe blistering or erythema | Strong sensitization; major changes needed |
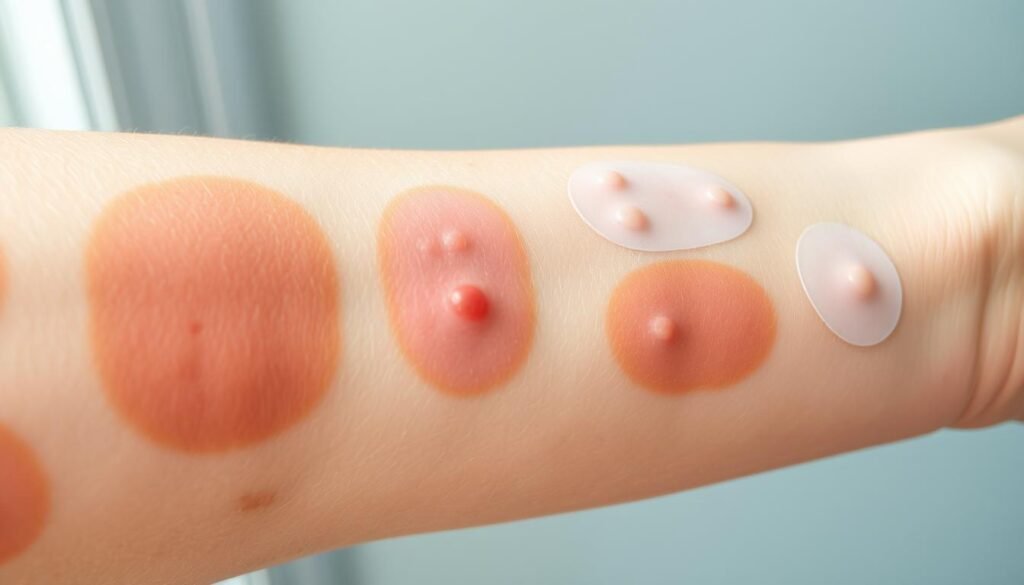
Combining patch test grades with the patient’s symptom history offers insights into allergens triggering their reactions. This allows dermatologists to craft custom treatment plans. Such strategies aim for the best management of allergic contact dermatitis.
Patch Testing Accuracy and Limitations
Patch testing is key for finding what causes skin allergies. It has a patch testing accuracy rate of 70-76%. This is when using a common set of allergens known as the European Standard Series. Most patients are covered by this series. It finds the cause of skin allergies in about 85% of them. Yet, there are times when patch testing doesn’t spot less common allergens.
False negatives and false positives are big hurdles. Drug patch tests for skin reactions have a 32-50% chance of spotting an issue. Some folks might need more checks 7 to 10 days later. This helps link the test results to what doctors see.
- Reactions in patch testing can vary significantly, including:
- Negative
- Irritant
- Uncertain
- Weakly positive
- Strongly positive
- Extreme
Complications are another worry. Dark skin might get dark spots that last for a while. Some meds, like antihistamines, can mess with the results. Patients often have to stop these meds 10 days before the test. This helps make sure the results are right.
Doing the patch test longer can find more allergens, 37-76% more, actually. About half of the allergens found aren’t in the standard test. Nickel sulfate is a common allergen for about 18.5% of people. A cobalt allergy might go hand in hand with allergies to chrome and nickel.
To handle allergic skin issues well, a full plan is needed. It may include meds, allergy shots, diet changes, and tweaking your surroundings. Knowing the limitations of patch testing is crucial. It helps doctors and patients make better choices for diagnosis.
Potential Side Effects of Patch Testing
Patch testing is key to finding what causes contact dermatitis. But, it can have side effects. Knowing these risks is crucial for those getting tested. About 5% of patients see side effects like rashes, high temperatures, and flare-ups.
Understanding Risks and Reactions
Responses to the test can differ in how strong and long they last. Side effects often include a mild burn or itch where the patches are. Sometimes, this can turn into severe itching or burning. “Angry back syndrome” might also happen. This is when a strong reaction makes the skin overreactive.
Reactions can take a while to fully show, often up to ten days. People with skin issues already should be extra careful. Flare-ups can come from the allergens or irritants used in the tests.
Doctors need to clearly tell patients about these side effects. They should say when it’s important to get medical help. If there’s strong itching, burning, redness, or pain, call your doctor right away. Knowing the risks helps people be ready. They can watch for reactions and act when needed.
| Side Effect | Occurrence Rate | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mild Burning | Common | Localized burning at patch sites |
| Itching | Common | Mild to moderate itching sensations |
| Severe Itching/Burning | Rare | Intense sensations requiring medical attention |
| Flare-up Reactions | 5% | Varying reactions such as rashes |
| Angry Back Syndrome | Rare | Hyper-reactivity in skin after a strong positive reaction |
Strategies for Allergen Avoidance Post-Patch Testing
Effective allergen avoidance is key after patch testing. This helps manage contact dermatitis. Clinicians give valuable advice based on your allergens. They aim to help you make better skincare choices.
Patient Education and Resources
Learning about allergens is crucial to avoid new allergic reactions. Dermatologists like Dr. Rishi at Parashar Skin Clinic stress this point. They provide materials on what to avoid and safer options. This boosts patient understanding and confidence.
The American Contact Dermatitis Society also offers help. They share lists of safe products and skincare tips. With this support, managing your skin health becomes easier.
| Allergen Type | Examples | Recommended Products |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | Nickel, Cobalt | Nickel-free jewelry, Protective gloves |
| Preservatives | Formaldehyde, Parabens | Paraben-free lotions, Natural skincare |
| Fragrances | Artificial fragrances | Fragrance-free products, Essential oils |
| Chemicals | Latex, Dyes | Latex-free gloves, Non-toxic dyes |
| Plant-based Allergens | Poison Ivy, Fragrance from flowers | Oatmeal baths, Skin barrier creams |
Knowing your allergens makes it easier to choose the right products. This leads to healthier skin habits. For more on self-care after patch testing, see this patient self-assessment study.
Conclusion
Patch testing is key in finding allergens that cause contact dermatitis. It is crucial to managing the condition. Around 1-year prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis at 7% underlines its importance. This testing helps identify specific allergens, like nickel and fragrances. It plays a big role in making personalized care plans.
Through patch testing, doctors make more informed decisions. It boosts patient education and health outcomes. A whopping 20% of the general population might react to contact allergens. This fact stresses the need for effective assessment, especially at work. Adopting a smart approach to skin health involves detailed testing. The advice is to keep test chambers on for 48 hours and check late results for the best insights.
To conclude, patch testing is essential in identifying harmful allergens and protecting people from them in the future. It helps doctors understand allergens better and improve treatment for skin allergies. This leads to better living standards for patients. For more info on patch testing’s rules and benefits, check this detailed article.