About 10% to 20% of infants in the U.S. develop atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema. It’s a chronic skin condition that causes a lot of discomfort. People from different backgrounds are affected. Up to 13% of Asian American and Pacific Islander groups and 11% among white people have it. Knowing the treatment options, both medical and home-based, is crucial for managing eczema well. Let’s dive into the ways to find relief, from moisturizing routines to cutting-edge medicines.
Gaining knowledge is the first step to managing atopic dermatitis effectively. Recognizing the signs, understanding what triggers it, and using conventional and alternative treatments helps. A comprehensive approach typically gives better results. This can lead to a better quality of life. From prescription creams to natural remedies, creating a successful treatment plan can really help alleviate symptoms and promote healthier skin.
Key Takeaways
- Atopic dermatitis affects 10% to 20% of infants, highlighting a significant need for effective treatment options.
- Utilizing moisturizers daily is crucial for managing skin hydration and preventing flare-ups.
- Home remedies, such as aloe vera and coconut oil, can provide additional relief.
- A personalized treatment plan developed with a dermatologist enhances effective eczema management.
- Identifying triggers, including certain fabrics and chemicals, can help prevent exacerbations.
- Advanced treatment options are available for severe cases that do not respond to typical therapies.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a common type of eczema. It affects millions in the United States. Over 31 million Americans have eczema, with atopic dermatitis being the most common. More than 9.6 million children and about 16.5 million adults suffer from this condition. It can cause severe dryness and irritation in children, leading to uncomfortable skin patches.
The cause of atopic dermatitis includes genetics and immune system reactions. Problems in the skin barrier can make the skin dry and itchy. Those with this condition may also have food allergies and asthma.
Environmental factors can make atopic dermatitis worse. Dust mites and harsh soaps can inflame the skin, making discomfort worse. Stress can also cause flare-ups, showing the link between emotional health and the condition.
To manage atopic dermatitis well, knowing what triggers it is key. It’s essential to take good care of your skin. Regular moisturizing and avoiding irritants help keep the skin healthy and reduce flare-ups. For more on this topic, read the Mayo Clinic’s guidelines.
Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, more commonly known as eczema, has many symptoms that can lower quality of life. Recognizing these symptoms early can help with better management and care.
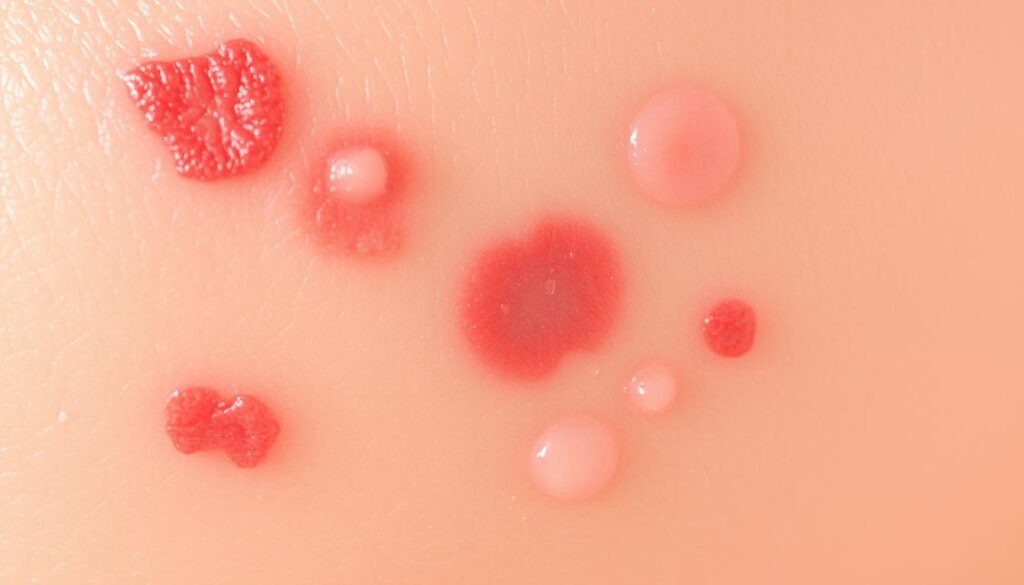
Recognizing Eczema Bumps
Eczema bumps look like small, raised spots on the skin. These eczema bumps might be itchy and change color with skin tone. They might ooze or form crusts, causing discomfort.
These bumps usually appear on the elbows, behind knees, or on other skin folds. Keeping skin moisturized and using topical treatments as suggested by a doctor can help manage them.
Identifying Atopic Dermatitis Rash
The atopic dermatitis rash varies in color, from red to dark purple. It makes the skin thick or scaly because of much scratching. In babies, this rash is often seen on the face and scalp.
For older kids and adults, it usually shows up in elbow and knee creases. The rash may come with dry skin, adding to the discomfort. For more details on dealing with atopic dermatitis, consider visiting this helpful site.
Diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis
Diagnosing atopic dermatitis starts with a detailed check by a healthcare provider. They chat about symptoms and medical past and look at the skin closely. It’s key to diagnose atopic dermatitis right to find the best treatment.
Health Care Provider Evaluation
The first check focuses on the patient’s eczema flare-ups and symptoms. Providers ask how bad it is, what the person’s life is like, and what treatments they’ve tried before. This helps figure out the triggers and make a plan that works.
Patch Testing for Allergens
Sometimes, doctors suggest skin tests, like patch tests, to find allergens that might be causing problems. This means going to the clinic several times for one week to put allergens on the skin. Two days later, they take off the patches and watch the skin for a few more days to see any allergic reactions.
If things still aren’t clear, a small skin sample might be taken. A skin expert looks at it in a lab to make sure it’s not another skin problem. This step gives important information to help manage the dermatitis better.
| Test Type | Description | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Patch Testing | Application of allergens to the skin to identify reactions | 3 visits over 1 week |
| Skin Biopsy | Removal of a skin section for examination | 3 to 7 days for results |
Figuring out the cause of eczema flare-ups through tests helps in managing them better. The right diagnosis means people can handle their symptoms well and live better lives.
For more details, check out the link here on atopic dermatitis diagnostics.
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Options
Managing eczema well is key for those with atopic dermatitis. Having a good treatment plan can help lessen symptoms, stop flare-ups, and make skin healthier. It’s crucial to moisturize well to keep the skin barrier strong.
Importance of Moisturizing
Moisturizers are crucial for eczema care. Applying emollients daily can lessen dryness and itching. It also helps prevent skin harm. Doctors suggest choosing products without fragrance to avoid irritation. Moisturizing well has many benefits:
- Restoring skin barrier function
- Preventing moisture loss
- Reducing the frequency of flare-ups
Medicated Creams and Ointments
Alongside moisturizers, there are medicated creams for atopic dermatitis. Some commonly used treatments are:
- Corticosteroids: These reduce inflammation and itching and are often first-line treatments during flare-ups.
- Pimecrolimus cream and Tacrolimus ointment: Good for moderate to severe cases, these are topical inhibitors.
- Crisaborole and Ruxolitinib creams: They are newer options for symptom control.
- Roflumilast cream: It’s designed for direct application as part of managing eczema.
A dermatologist who is board-certified can identify the best meds for each person. Using these creams correctly can greatly better symptoms and skin health.
Medications for Severe Cases
People with severe atopic dermatitis often need stronger treatments. Over-the-counter options or standard treatments might not be enough. In such cases, certain medications offer hope for relief.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors
Topical calcineurin inhibitors, like tacrolimus (Protopic) and pimecrolimus (Elidel), are good for treating severe eczema. They help by stopping immune responses that cause inflammation in the skin. These treatments are applied once or twice a day.
People can start to feel better between one to six weeks. These inhibitors are safer for long-term use than corticosteroids. They have fewer side effects over time.
Oral Medications for Inflammation
When creams and lotions aren’t enough, doctors may recommend pills like cyclosporine or methotrexate. These are taken once or twice a day. They play a key role in managing severe eczema symptoms over weeks or months.
Although oral corticosteroids work fast, they pose risks like high blood pressure and weaker bones. So, picking the right medicine carefully is crucial for long-term eczema control.
Alternative Treatments and Therapies
People with atopic dermatitis often try different alternative eczema treatments. These methods can add to standard treatments, helping control symptoms. Natural eczema remedies are popular for their easy access and mild effects.
Coconut oil can cut down staph bacteria on the skin, which helps prevent infections. It also moisturizes the skin, offering a two-fold benefit for eczema sufferers. Another good choice is topical vitamin B12. Studies show it can lessen eczema symptoms in both adults and children.
Looking into Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) might bring some relief. TCM uses acupuncture, acupressure, and herbal remedies that are personalized. Ayurveda, an Indian practice, uses herbs, oils, and activities like yoga. It aims to achieve overall balance and wellness.
Using mindfulness techniques like yoga and Tai Chi can cut stress, a known eczema trigger. These methods might reduce inflammation and provide some peace. Acupressure has been effective in easing itchiness and thick skin. Massage therapy can also reduce stress and eczema outbreaks.
Wearing the right clothes is crucial; cotton and silk can keep you comfortable. They help manage itching with their moisture-wicking features. Therapies like climatotherapy let patients heal in certain climates. Another interesting approach is balneotherapy, which involves soaking in mineral-rich waters to help the skin.
Bathing in the Dead Sea has been shown to help eczema. Hydrotherapy spas, like Avène in France, also offer positive effects on life quality for those with atopic dermatitis. With ongoing research, new treatments keep appearing, providing more choices for those exploring alternative options.
Eczema Triggers and Prevention
Identifying eczema triggers is key to managing atopic dermatitis. Many environmental factors can make the skin irritated. Knowing these triggers and using prevention strategies can make flare-ups less severe and frequent.
Environmental Factors Affecting Skin Irritation
Environment plays a big role in skin irritation for those with atopic dermatitis. Important factors include:
- Cold or dry weather, which often leads to moisture loss in the skin.
- Fabrics such as wool or synthetic fibers that can irritate sensitive skin.
- Household irritants like soaps, detergents, and cleaning products.
- Outdoor allergens such as pollen and dust mites.
- Stress, which can worsen symptoms through physiological responses.
Common Eczema Triggers to Avoid
There are specific triggers to avoid for fewer eczema flare-ups. They include:
- Contact allergens: These may include certain metals, latex, and specific personal care products.
- Food allergies: Common allergens such as dairy, eggs, and nuts can trigger flare-ups in sensitive individuals.
- Hormonal changes: Fluctuations, particularly during menstruation, can lead to heightened symptoms.
- Skin infections, which can provoke itching and worsen inflammation.
- Exposure to temperature extremes, whether hot or cold, which can alter skin moisture levels.
Home Remedies for Atopic Dermatitis
Exploring home remedies for eczema can offer comfort from the discomfort atopic dermatitis brings. Many look towards natural options for better skin hydration and less inflammation. Among these, coconut oil is known for its ability to lock in moisture and get absorbed quickly. This helps restore the skin’s barrier. Aloe vera gel also acts as a soothing agent. It helps relieve itching and aids in healing irritated skin.
Coconut Oil and Aloe Vera Benefits
Coconut oil not only moisturizes but also eases eczema symptoms. It has anti-inflammatory properties that reduce redness and irritation. This makes it a favorite among those looking for natural relief. On the other hand, aloe vera is great for its cooling effects, especially on sensitive infant skin. Together, they offer strong support for daily skin care routines. They help manage eczema flare-ups effectively.
Utilizing Colloidal Oatmeal Baths
Colloidal oatmeal baths are another outstanding remedy for eczema. They’re especially good for soothing irritated skin. A lukewarm bath with colloidal oatmeal restores the skin barrier and reduces inflammation. This gentle method is especially helpful for infants with eczema. It provides a soothing experience that lessens dryness and itching. By adding these natural treatments to daily routines, individuals can improve their skin health. This helps lessen the effects of atopic dermatitis.