Did you know more than 31 million Americans have eczema? People often mix up terms like atopic dermatitis and eczema. However, they mean different things in the world of skin conditions. Atopic dermatitis is the most common kind of eczema. It affects around 16.5 million American adults and above 9.6 million children. Knowing the difference between these two can help manage the condition better.
We will explore what makes eczema and atopic dermatitis distinct. This includes their symptoms, causes, and types. The goal is to clear up confusion about dermatitis inflammation. After reading this, you should understand these conditions better. This understanding will arm you to face the challenges they bring.
Key Takeaways
- Eczema impacts over 31 million people in the United States.
- Atopic dermatitis is a prevalent form of eczema affecting millions.
- Understand the various types of eczema, including atopic dermatitis.
- Recognize that while atopic dermatitis can start in early childhood, it may persist into adulthood.
- There is currently no cure, but effective treatments can alleviate symptoms.
Understanding Eczema
Eczema is about different conditions that cause skin inflammation. It shows as rashes, itchiness, and dry skin. Over 31 million Americans deal with some kind of eczema. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type, affecting an estimated 26.1 million people in the U.S.
People feel eczema in various ways. Sometimes, flare-ups occur now and then. Other times, they happen often and can last weeks. Things like pollution and extreme weather lead to eczema.
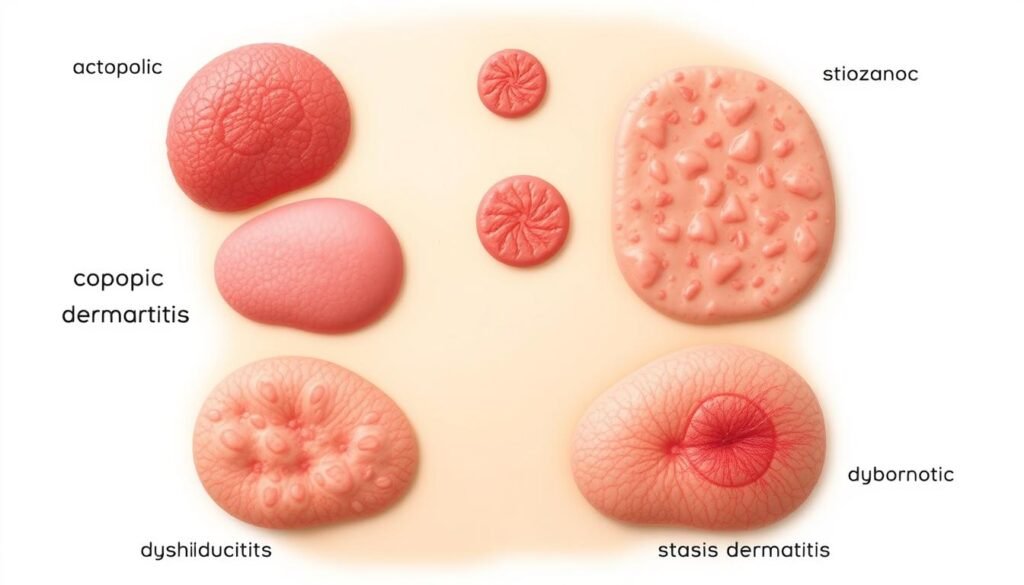
There are seven main eczema types. Each one has its own signs and triggers. Allergic contact dermatitis happens due to certain things like soaps or metals. Dyshidrotic eczema causes small, itchy blisters on hands and feet. Nummular eczema looks like round patches on the skin. It’s important to know which type you have to manage it right.
Besides atopic dermatitis, there’s seborrheic dermatitis which affects oily spots, and stasis dermatitis from bad leg circulation. Knowing the differences is key for good treatment. For more on atopic dermatitis versus eczema, read this helpful article.
| Eczema Type | Common Symptoms | Potential Triggers |
|---|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | Itchy, dry skin; red patches | Pollutants, allergens |
| Contact Dermatitis | Red, itchy rash; blisters | Soaps, metals |
| Dyshidrotic Eczema | Itchy blisters on hands/feet | Heat, stress |
| Nummular Eczema | Round, coin-shaped spots | Dry skin, irritants |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Scaly patches, dandruff | Oily skin, stress |
| Stasis Dermatitis | Swelling, redness, itchy rash | Poor circulation |
Learning about these eczema types helps in pinpointing them. It also helps create treatments that work for each person.
What is Atopic Dermatitis?
The atopic dermatitis definition shows it’s a common eczema form, hitting mainly young kids. It shows up on the body, especially in elbow and knee creases or on infant faces and scalps. As a chronic skin issue, it leads to dry skin, severe itching, and sometimes oozing or crusting rashes.
Symptoms vary widely from person to person, with some seeing flares and calm periods. It usually starts before five years old. Yet, it can affect folks into their teens and adulthood. Risk factors include a history of allergies, asthma, or hay fever. It can bring extra problems like skin infections or trouble sleeping.
This condition isn’t catching but stems from genetic links. It’s part of “atopic” disorders that also list asthma and hay fever. Those affected often react more to environmental triggers. While no clear cure exists, treatments can ease symptoms, helping people have a better quality of life.
Key Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, often called eczema, shows symptoms that change daily routines. The main sign is very itchy skin. This itchiness appears suddenly and can be intense. Scratching the itchy area can cause a rash that spreads over various body parts. The areas become red and swollen, adding to the discomfort.
Common atopic dermatitis symptoms are:
- Dry skin, mostly in skin folds
- Small, rough bumps like acne
- Color changes in the skin, with dark areas on darker skin tones
- Blisters that may leak fluid and then form a crust
- Thick, leathery skin patches
Symptoms can differ with age and skin color, with dry skin and itchy skin worsening over time. Babies often get eczema on their cheeks and forehead. Older children may see it on elbows and knees. Adults might get flare-ups on their hands or near their eyes.
Flare-ups can happen now and then, affecting different parts of the body each time. Managing symptoms helps with skin health and eases anxiety linked to the disease. For more details on atopic dermatitis, click on this link.
Knowing these symptoms early and starting treatment can make a big difference. It helps improve life quality for those with atopic dermatitis. For more on treatments and care, visit this page.
Recognizing Eczema Symptoms
Spotting eczema early is key to managing it well. Symptoms vary widely among people and eczema types. Look for inflammation, redness, swelling, and lasting itchiness to spot this skin issue early. Recognizing these signs helps start the right treatment sooner.
Eczema affects over 31 million Americans, highlighting the need to notice flare-ups quickly. Atopic dermatitis hits 16.5 million adults and 9.6 million kids in the U.S. Also, 12% of people deal with neurodermatitis, with Black Americans often facing harsher symptoms.
To help spot eczema, here’s a detailed list of common symptoms:
| Symptom | Description |
|---|---|
| Itchiness | Intense itching is a clear sign of eczema. |
| Dryness | Skin looks dry and might feel rough or flaky. |
| Redness | Red, inflamed areas show skin is irritated. |
| Swelling | Scratching or contact with irritants can swell the skin. |
| Scaling and Crusting | Patches might crust or scale, sometimes bleeding. |
| Discoloration | Dark or brown patches appear on those with darker skin. |
Eczema can look different depending on skin type, especially in darker tones. It may appear as gray or brown patches, making diagnosis hard. Often, eczema shows up on elbows, knees, hands, and babies’ and toddlers’ faces.
Some people see skin color changes even after eczema goes away. Stress, hormonal shifts, and changes in temperature can also cause flare-ups. It’s important to track when and why symptoms get worse.
Atopic Dermatitis vs Eczema: What’s the Difference?
People often mix up the terms atopic dermatitis and eczema. Knowing the difference helps us understand skin conditions better. Atopic dermatitis is a type of eczema. However, eczema is a broad term that covers many skin issues.
It’s crucial to know that while all atopic dermatitis is eczema, not all eczema is atopic dermatitis. This knowledge is important for treating and managing the conditions.
Defining the Terms
Atopic dermatitis is a long-term skin problem that causes inflammation, redness, and itching. It often starts in childhood. In the U.S., over 16.5 million adults and 9.6 million kids have it.
Eczema includes different kinds like contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis. So, eczema represents more skin problems. For more details, check this article.
Underlying Causes
Many factors lead to eczema, especially in those with a history of allergies or asthma. Genetics play a big role in getting atopic dermatitis. Things like irritants also make it worse.
Keeping skin moist and avoiding triggers are key to control it. Studies show that using lotion on babies can prevent atopic dermatitis. Knowing these causes is key for those affected by these conditions.
| Aspect | Atopic Dermatitis | Eczema |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A chronic inflammatory skin condition | A broader term for various inflammatory skin conditions |
| Age of Onset | Typically in childhood | Can occur at any age |
| Common Symptoms | Itching, redness, inflammation | Varies by type; may include itching, redness |
| Treatment | Topical steroids, moisturizers | Varies; can include antihistamines, steroids |
Types of Eczema
Eczema has many distinct types, each with unique symptoms and triggers. Knowing these can help manage your specific eczema better. From atopic dermatitis to contact dermatitis and seborrheic dermatitis, this section explores each type. It offers a clearer view of dermatitis types linked with eczema.
Understanding Different Types of Eczema
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common eczema type, it often starts in childhood. It mainly affects the face, hands, feet, inner elbows, and behind the knees.
- Contact Dermatitis: This type comes from touching irritants or allergens. It splits into allergic and irritant categories.
- Dyshidrotic Dermatitis: Known by small blisters on the hands and feet. Cool compresses and topical steroids help treat it.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Also called scalp eczema, it causes oily patches and flaky skin, mainly on the scalp.
- Neurodermatitis: Leads to severe itching and thick skin patches from constant scratching.
- Nummular Dermatitis: Features round, coin-shaped spots and tends to affect men more, especially in midlife.
- Stasis Dermatitis: Seen in people with poor circulation, it’s due to fluid leaking from veins. This causes swelling and skin discoloration.
Knowing these eczema types is key for the right management approach. Treatment for eczema varies, so understanding your specific type is crucial.
| Type of Eczema | Main Characteristics | Treatment Options |
|---|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | Common in children; affects face, hands, feet | Moisturizers, steroids |
| Contact Dermatitis | Caused by irritants or allergens | Avoiding triggers, topical steroids |
| Dyshidrotic Dermatitis | Small blisters on hands and feet | Cool compresses, steroid creams |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Scaly, oily patches on scalp | Medicated shampoos, topical treatments |
| Neurodermatitis | Itchy areas leading to thick patches | Stop scratching, topical steroids |
| Nummular Dermatitis | Round, coin-shaped spots | Topical treatments |
| Stasis Dermatitis | Swelling due to poor circulation | Compression stockings, elevation |
Common Triggers of Atopic Dermatitis
Knowing what causes atopic dermatitis flare-ups is key to handling the condition well. There are main triggers: irritants, allergens, and the environment around us. Recognizing them is the first step for anyone wanting to keep their skin calm and healthy.
Things like soaps, detergents, and perfumes often start outbreaks. Those troubled by these irritants might see their skin get dry and inflamed. This leads to discomfort. Also, being in cold or less humid weather can make the situation worse, causing more serious flare-ups.
Allergens are big troublemakers too. Common ones include dust mites, animal fur, and pollen. They mostly affect those who already deal with allergies. Between 73% and 88% of people with atopic dermatitis feel the impact of these allergens. Foods, such as dairy or eggs, can also set off symptoms for some.
Stress and hormone changes can make eczema worse too. Many with the condition say they struggle more when they’re stressed. Plus, sudden changes in weather can irritate and upset their skin.
Learning about these triggers lets people find ways to avoid them. Regular use of moisturizers, staying away from irritants, and keeping stress low help a lot. By watching closely, they can manage their eczema better and enjoy life more comfortably.
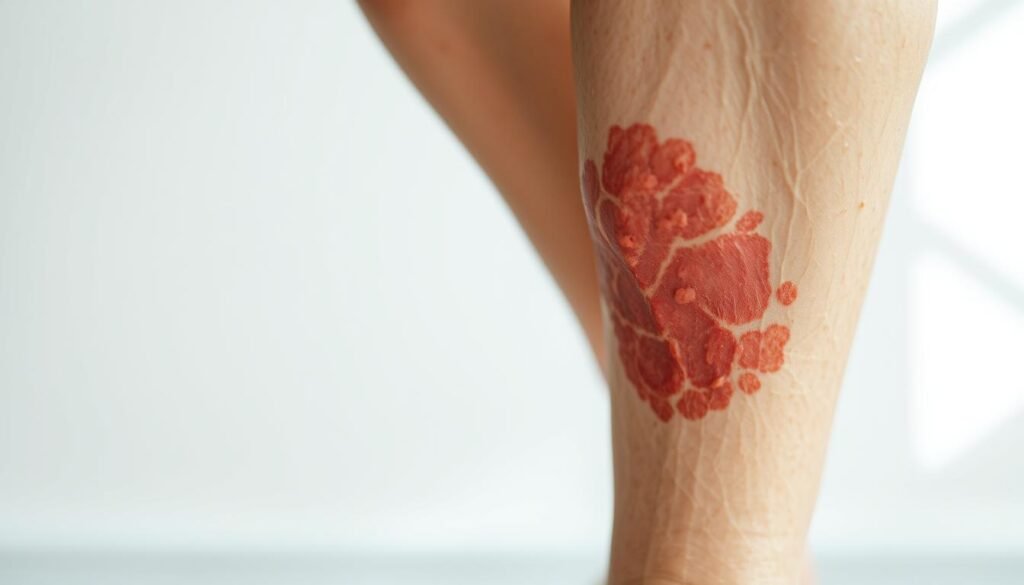
Leg Eczema: A Common Manifestation
Leg eczema can cause discomfort and major skin problems. It often shows up on the legs, leading to symptoms that disrupt everyday life. Knowing about leg eczema helps in taking care of it properly.
Spotting an itchy legs rash early can lead to faster treatment. This is crucial for maintaining good skin health.
Eczema on Legs and Leg Inflammation
Eczema on the legs can cause various types of inflammation. This includes redness, swollen skin, and tenderness. Here are common signs:
- Red patches that might also be dry
- Thickened skin that could end up cracking
- Swelling that might spread out
Leg eczema doesn’t just change how the skin looks. It can also lead to more severe issues if not treated. Scratching a lot can break the skin, causing infections.
Itchy Legs Rash: Understanding Symptoms
Knowing the symptoms of an itchy legs rash is important for anyone with leg eczema. The rash usually has these characteristics:
- Intense itching that gets worse at night
- Flaky or scaly patches showing dry skin
- Small bumps that might leak fluid if scratched
This knowledge helps people recognize leg eczema. Getting the right diagnosis is crucial. It helps lessen the effect of this condition on life quality.
Leg Eczema Treatment and Management
Handling leg eczema needs a well-rounded strategy covering both quick relief and ongoing care. Many try out different treatments to find relief and prevent more flare-ups. This part talks about working treatments and stresses keeping the skin moist as key for better care.
Effective Treatments for Leg Eczema
For those battling leg eczema, many treatments are available. Doctors might suggest:
- Corticosteroid creams: They lower swelling and are usually used once or twice a day.
- Calcineurin inhibitor creams: These creams treat symptoms without the risks of long-term steroid use.
- Oral medications: Medicines like dupilumab are for moderate to severe cases, helping with ongoing control.
- Light therapy: Sunlight or artificial UV can help if other treatments don’t work.
Home remedies are also important for care. Soaking in an oatmeal bath, using wet wraps, and applying anti-itch creams can offer relief.
Moisturizing Legs for Better Skin Care
Moisturizing is vital for people with leg eczema. It strengthens the skin’s barrier, helping to cut down on flare-ups. Tips include:
- Applying a thick moisturizer twice daily to keep moisture in.
- Choosing lotions with ceramides to help the skin barrier.
- Trying a diluted bleach bath to kill skin bacteria.
Maintaining a moisturizing routine is crucial. It keeps the skin from getting dry and itchy. Doing this makes life better for those with leg eczema.
Preventive Measures for Eczema and Dermatitis
Taking steps early is crucial for stopping eczema and caring for dermatitis. Around 31 million Americans deal with eczema. Of these, more than 7% of adults have atopic dermatitis. To reduce symptoms and prevent flare-ups, it’s important to care for your skin well. This means moisturizing often, finding out what triggers your eczema, and handling stress better.
It’s vital to have a good skincare routine. You should use gentle cleansers and moisturize every day. Keeping your skin hydrated can make flare-ups less severe and keep your skin healthy. A lot of experts agree that staying moisturized helps a lot with eczema management. Moisturizing well is very important for taking care of eczema.
Avoiding things that irritate your skin can really help prevent eczema. Some irritants are certain types of cloth, soaps, and items used around the house. It’s also good to keep your living space clean from dust mites and pet dander. Figuring out what specifically triggers your eczema and staying clean are key for long-term dermatitis care.

Making changes to your lifestyle is also key in stopping flare-ups. Lower your stress with relaxation techniques and stay active. Paying attention to things like changes in the weather and allergens in your environment can help you avoid flare-ups. These steps help you come up with good preventive measures.
The table below shows triggers and how to avoid them:
| Trigger | Preventive Strategy |
|---|---|
| Pollen | Limit outdoor activities during high pollen seasons |
| Temperature changes | Dress in layers to regulate body temperature |
| Rough fabrics | Opt for soft, breathable materials such as cotton |
| Household products | Choose hypoallergenic, fragrance-free options |
| Animal dander | Keep pets out of bedrooms and clean regularly |
| Stress | Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation |
Learning about good skincare and knowing what triggers to avoid are big steps towards stopping eczema. By acting early and carefully, managing eczema can become easier for many people.
Conclusion
It’s key to know the difference between atopic dermatitis and eczema for good skin care. Eczema is a general term, but atopic dermatitis is a specific kind with its own signs and things that make it more likely to happen. The medical world talks more about atopic dermatitis because it’s important in skin studies, but eczema can mean many different skin problems.
Spotting the signs early and getting help soon can make a big change in how your skin feels and looks. Atopic dermatitis is linked to some health issues like being overweight, having diabetes while pregnant, and where you live or work. Knowing about these links helps in taking better care of yourself or someone with these skin issues.
To sum it up, both people and doctors need to stay updated on atopic dermatitis and the various types of eczema. Watching out for symptoms and taking action early leads to healthier skin. This journey to better skin care can make life better in many ways.