Eczema, or atopic dermatitis, impacts nearly 10% of people in the U.S. That’s about 31.6 million folks! It usually starts in childhood, with 1 in 4 kids showing signs before turning five. Knowing the early symptoms is key to manage this skin condition well.
Symptoms vary a lot from one person to another. They can include itchy and dry skin, along with unique rashes. It’s crucial to spot and keep an eye on these signs early. Not doing so can cause a lot of discomfort and further issues. It helps to know how this condition appears in different ages and skin types.
For deeper insights on what symptoms to look for, check out more on the symptoms and causes of atopic dermatitis. Being proactive and well-informed lets people better handle their skin health.
Key Takeaways
- Atopic dermatitis affects around 31.6 million individuals in the U.S.
- Symptoms often start in childhood, impacting 1 in 4 children.
- Identifying symptoms like itchy skin and dry patches is crucial for management.
- Untreated eczema can lead to significant discomfort and complications.
- Understanding triggers and symptoms can aid in effective care strategies.
Understanding Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, known as eczema, affects over 17.8 million Americans. It often starts in childhood, within the first six months. For most, itching is an everyday battle.
This condition breaks down the skin’s protective layer. This makes the skin more sensitive to irritants and allergens. If a child has eczema, there’s a 30% chance they could get asthma.
To manage eczema, it’s vital to avoid triggers and follow a regular bath and moisturize routine. Good sleep, a healthy diet, and stress management are also key. Treatment options include creams, non-steroidal products, and biologics for tough cases.
It’s important to understand this condition’s complexity and its link to allergies like asthma and hay fever. Knowing what causes flare-ups and how to manage skin sensitivity can help those affected lead better lives.
Common Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis can greatly affect one’s quality of life. It’s important to know the symptoms to manage them early. Symptoms include itchiness, dry skin, and characteristic rashes. Each symptom adds to the discomfort of those with the condition.
Itchy Skin and Its Impact
Itchy skin is a major problem for those with atopic dermatitis. The itch leads to scratching, which makes things worse. This can cause inflamed skin and more discomfort. Fighting the urge to scratch is a daily battle for many.
Dry Skin Patches
Dry skin patches are common in atopic dermatitis sufferers. These patches can be severe and may lead to cracking skin. Things like low humidity and frequent washing can make dryness worse. Moisturizing well is key to easing dry patches and irritation.
Rash Characteristics
Rashes from atopic dermatitis vary in appearance. You might see red, flaky patches that ooze or crust, especially on lighter skin. Those with darker skin might see their skin darken after a flare-up. Knowing these signs is critical for quick treatment.
Identifying Eczema Flare-ups
Eczema flare-ups show up in different ways. It’s key for folks to spot familiar triggers and know how often and long they happen. Learning to recognize these flare-ups can really help control symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
Common Trigger Areas
Flare-ups often hit certain body spots, especially where skin folds. Usual spots include:
- Behind the knees
- Elbows
- Armpits
- Neck
- Hands and feet
Things like emotional stress, surroundings, and certain soaps or materials can make these areas worse. Changing daily habits and environments to avoid these triggers can help stop flare-ups.
Frequency and Duration of Flare-ups
How often and how long eczema flare-ups last varies by person. Some might have sudden, severe outbreaks that last days to weeks. Notably:
- Flare-ups can come and go for some, while others may have long-lasting irritation.
- Finding patterns in your flare-ups can help manage them better.
Being able to track and make sense of these changes lets people tackle their eczema head-on. This can greatly enhance their life quality.
| Type of Trigger | Examples | Effect on Skin |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Dry air, temperature changes | Increases dryness and irritation |
| Physical | Wool fabrics, rough materials | Causes rashes and itching |
| Emotional | Stressful situations | Can prolong flare-ups |
| Chemical | Household cleaning products, fragrances | Leads to skin irritation and redness |
Physical Appearance of Affected Skin
The look of skin with atopic dermatitis changes depending on a person’s skin color. Knowing these changes helps doctors diagnose and treat it right. Different signs can show up on the skin, telling us about rashes and skin health.
Red Rashes on Light Skin
People with light skin often see bright red rashes. These rashes stand out with oozing and crusting. This bright color means inflammation and irritation, helping spot the issue early.
Darkened Areas on Darker Skin
On the other hand, those with darker skin might see dark patches. These spots can itch and feel sore without looking red. It’s key to know this to avoid wrong diagnoses. Correctly spotting these signs makes sure people get right treatment for their skin issues.

| Skin Tone | Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Light Skin | Bright Red Rashes | Oozing, Crusting |
| Darker Skin | Darkened Areas | Itchy, Inflamed |
Skin Irritation and Inflammation
Atopic dermatitis makes the skin really red and itchy. Starting treatment early helps avoid more problems and keeps your skin healthy.
Symptoms of Inflamed Skin
People with inflamed skin might see several signs, like:
- Swollen patches that are tender
- Warmth in the affected spots because of more blood flow
- Sensitivity that makes daily tasks uncomfortable
It’s important to notice these symptoms early. They can lead to worse issues. Taking care of your skin early helps stop the pain and keeps the condition from getting bad.
Importance of Recognizing Skin Irritation
Knowing when your skin is irritated is key if you have atopic dermatitis. Not paying attention to early signs can lead to a bigger outbreak and problems like:
- Being more likely to have allergic skin reactions
- Long-term inflammation that damages the skin barrier
- The chance of lasting damage and scars
Being aware of these symptoms helps you care for your skin better. It means less severe flare-ups and healthier skin over time.
Recognizing Chronic Symptoms
Chronic symptoms of atopic dermatitis change how skin looks. It’s crucial to know these changes for proper care. One common outcome is thickened skin from constant scratching. Named lichen simplex chronicus, it gives skin a rough, leather-like feel.
Thickened Skin Over Time
Continuous irritation transforms the skin, leading to thickened patches. These areas feel rough. It shows how the body reacts to endless scratching and inflammation. Spotting this symptom early can guide people towards the right care methods.
Hyperpigmentation and Hypopigmentation
Skin color changes also accompany chronic atopic dermatitis. People might see darker spots, known as hyperpigmentation, after flare-ups. Or lighter areas, called hypopigmentation, where the skin has healed. Both can affect how one feels about themselves and need regular care strategies.
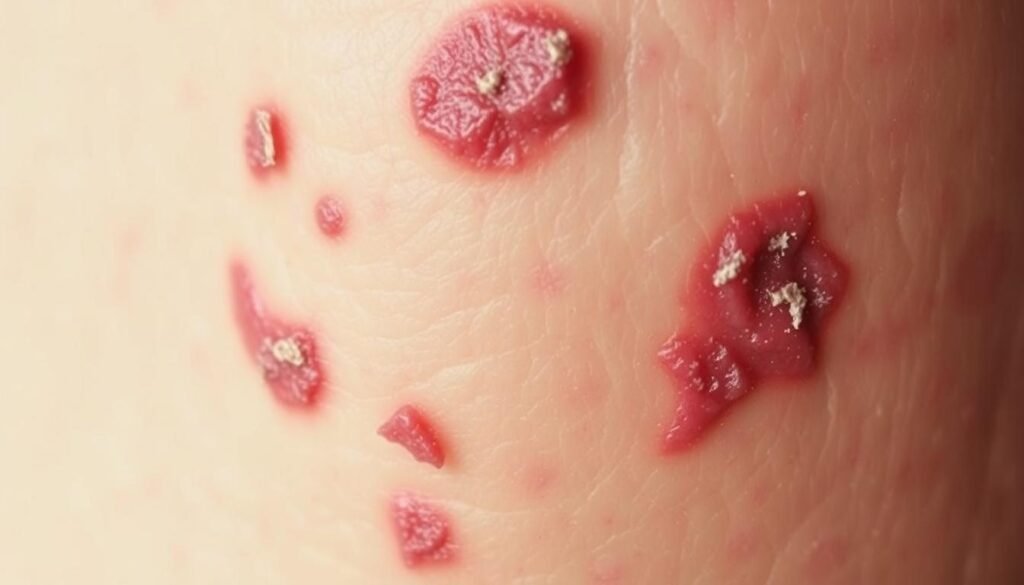
| Symptoms | Description | Long-term Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Thickened Skin | Rough, leathery texture due to frequent scratching | May lead to discomfort and increased risk of skin infections |
| Hyperpigmentation | Darkened skin in areas affected by chronic dermatitis | Can affect appearance and self-confidence |
| Hypopigmentation | Lighter patches where skin has healed | May cause distress regarding uneven skin tone |
Genetic and Environmental Triggers
Exploring the causes of atopic dermatitis shows the link between our genes and our surroundings. People with family members who have allergies, asthma, or eczema are more likely to get it. The FLG gene, which helps our skin protect us, plays a big role.
Some kids with bad eczema have changes in this gene. Those changes make their allergic skin reactions worse. This leads to constant itching and makes treating the skin harder.
Family History of Allergies
There’s a strong chance of getting atopic dermatitis if your family has a history of allergies. Genetics make people even more prone to it. Knowing your family’s health history helps identify things that make symptoms worse.
Common Environmental Triggers
Many things around us can trigger atopic dermatitis:
- Dust mites
- Pet dander
- Harsh chemicals in cleaning products and cosmetics
- Extreme weather conditions
- Pollution
Avoiding these triggers is key to controlling the condition. It’s also good for your skin’s health. Learn more about what triggers atopic dermatitis here.
Keeping your skin care consistent and seeking expert advice is important. This makes it easier to manage your skin’s health.
Complications Associated with Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis can lead to many complications beyond just skin issues. It makes you more likely to get skin infections. This is because damaged skin is an open door for bacteria, especially Staphylococcus aureus. Between sixty to ninety percent of people with this skin condition have staph bacteria on their skin. This makes their condition worse by adding infections.
People with atopic dermatitis can also catch viruses easier, such as the herpes simplex virus. This virus can turn into a serious problem known as eczema herpeticum, which causes painful blisters and more skin problems. The constant itchiness and discomfort can also make you feel stressed or depressed. Sadly, many deal with mental health issues like anxiety and depression due to these struggles.
This skin condition can also mess with your IgE levels, tricking allergy tests. This might lead to you cutting out foods you don’t really need to avoid. This can cause nutrition problems. Fernanda Young, M.D., did a study on how IgE levels can false alarm for food allergies in those with high serum IgE.
To tackle atopic dermatitis and its complications, following treatment plans and keeping clean is crucial. This helps manage symptoms and lowers the risk of further issues. For more tips on dealing with atopic dermatitis long-term, check out this resource.
| Complication | Details |
|---|---|
| Skin Infections | Increased risk of bacterial, viral, and fungal infections; common bacteria include Staphylococcus aureus. |
| Eczema Herpeticum | Severe skin condition caused by herpes simplex virus 1 in individuals with eczema. |
| False-positive Food Allergies | High IgE levels leading to unnecessary dietary restrictions. |
| Mental Health Issues | Increased risk of anxiety and depression due to chronic discomfort and stress. |
| Asthma and Allergies | Higher likelihood of developing asthma and allergic rhinitis. |
Management Strategies for Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
Managing atopic dermatitis requires a unique mix of skincare and the right meds. It first appears in childhood and calls for detailed skincare routines. Moisturizing well is key to stop the “itch-scratch cycle” which can make things worse. Stick to using products without fragrance and non-soap cleansers. Also, bathe daily to help strengthen the skin barrier and make it healthier.
Skincare Routines to Follow
Using emollients every day is crucial for dealing with atopic dermatitis. For mild cases, moisturizers alone can work. But in severe cases, adding ointments or creams for treatment is necessary. Always apply topical corticosteroids twice a day until you see better results. Ointments are more effective for flare-ups. Also, consider wet-wrap therapy with antihistamines at night for more relief.
Medications and Therapies
Meds play a key role in managing swelling and reducing itchiness. Medications for atopic dermatitis include topical calcineurin inhibitors, an alternative to corticosteroids. For worse eczema, drugs like dupilumab or JAK inhibitors might work well. Phototherapy is another option to help improve skin condition. Using all these strategies can help control symptoms and better the life of those with atopic dermatitis.