Did you know more than 31 million Americans suffer from eczema? This affects their daily routines and skin condition. Eczema bumps are quite common, more than you might realize. Eczema isn’t just a children’s issue; many adults deal with it too. They face ongoing flare-ups and discomfort. Knowing what causes skin inflammation from eczema and how to treat it can help sufferers. They can improve their life quality this way.
This article is a detailed guide on eczema. It covers the types of eczema, what triggers it, and how to manage it. It includes the newest eczema treatment options. Understanding eczema helps not just the ones fighting it, but raises overall awareness. This can help many struggling with this tough skin issue.
Key Takeaways
- Eczema affects over 31 million people in the United States, including many adults.
- Atopic dermatitis is the most common type and often starts in childhood.
- There is no cure for eczema, but there are ways to treat and manage it.
- Eczema can be triggered by things like allergies and stress.
- Knowing about different eczema types helps with the right diagnosis and treatment.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a term for many inflammatory skin conditions. They cause itchiness, dryness, and rashes. Atopic dermatitis is the most common type. This issue can start in childhood and might continue into adulthood.
Eczema isn’t catching. But, things like allergens can impact it. The eczema definition includes types like discoid and dyshidrotic eczema. Each has its own symptoms and triggers.
Flare-ups mean dry skin, raised bumps, and sometimes oozing. The symptoms can get pretty bad. Everyone’s triggers are different.
Genes can affect your chances of getting eczema. Those with family histories of allergies or asthma are more likely to get it. So, knowing your triggers and maintaining good skin care is key.
Understanding Eczema Bumps
Eczema bumps are a symptom of atopic dermatitis and other forms. These bumps are small, raised, and inflamed. They cause discomfort and make the skin look irritated. Knowing about these symptoms is key to manage them well. This is because they can look different on everyone.
Definition and Symptoms
Eczema bumps appear as small, itchy spots on the skin. People with these bumps feel very itchy. They might also have dry skin or see oozing. Eczema bumps symptoms should be spotted early. This helps in finding the right treatment. Over 31 million Americans live with eczema. It affects both kids and adults.
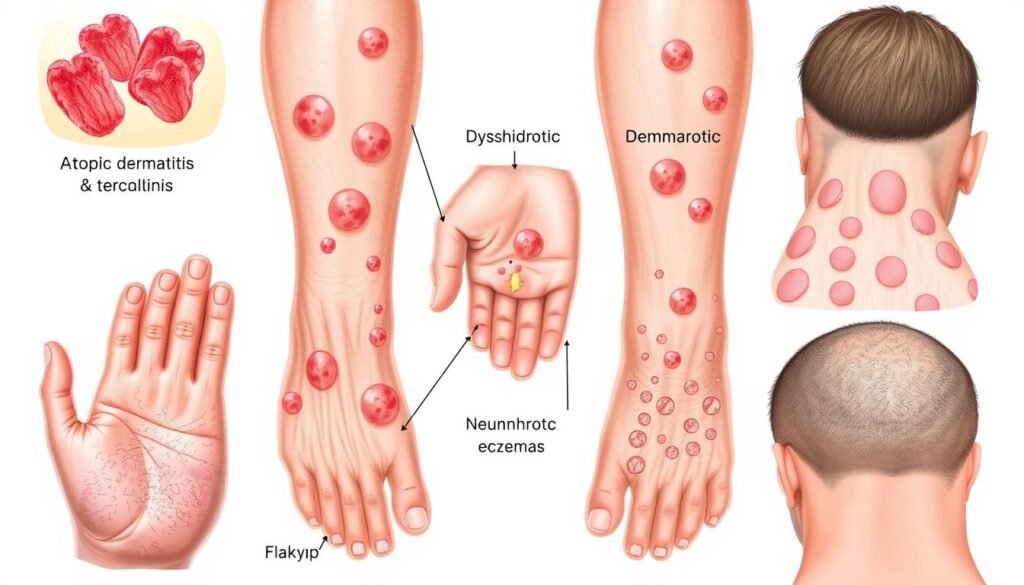
How Eczema Bumps Present On Different Skin Types
The look of eczema bumps changes with skin tone. Light skin shows red or inflamed bumps. But, darker skin might show bumps as brown, violet, or gray. This shows how atopic dermatitis can look different. African Americans may have more severe symptoms. They might see more thickening of the skin or bumpy texture.
A study found that genes and the environment can make eczema worse in people of color. Things like pollen, smoke, and chemicals in products are common triggers. Knowing these differences helps in treating eczema better. For more info, check this resource.
| Skin Type | Eczema Bumps Appearance | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Lighter Skin | Red inflamed bumps | Itching, dryness, potential oozing |
| Darker Skin | Brown, violet, or ashen bumps | Itching, dryness, thickened skin |
Types of Eczema
Eczema includes many skin conditions that cause redness and irritation. Knowing the different types helps manage and treat it. There are seven main kinds, each with its own symptoms and causes.
Common Types and Their Symptoms
Different eczemas have specific signs. Below is a summary of the major types and their symptoms:
| Type of Eczema | Common Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Atopic Dermatitis | Itchiness, dry patches, often appears in joint areas |
| Contact Dermatitis | Red, itchy rash; swelling; blisters |
| Dyshidrotic Eczema | Small, fluid-filled blisters on hands and feet |
| Neurodermatitis | Thickened, itchy patches in localized areas |
| Nummular Dermatitis | Coin-shaped patches of itchy, dry skin |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | Flaky, scaly patches on scalp, face, and body |
| Stasis Dermatitis | Swelling, weeping, and brown staining in lower legs |
Atopic Dermatitis: The Most Common Type
Atopic dermatitis is very common and usually starts in young kids. Those with asthma or hay fever might be more likely to get it. Signs include severe itching and dry skin, especially where the skin bends. Keeping the skin moist and avoiding certain things can help control it.
Causes of Eczema Bumps
Eczema bumps come from both genetic and environmental factors. It’s key to know these causes for better control and treatment.
Genetic Factors Contributing to Eczema
Our genes have a big part in eczema. If your family has a history of eczema or allergies, you might get it too. Changes in the filaggrin protein make the skin weak. This can lead to more moisture loss and irritation, increasing eczema risk.
Environmental Triggers That Ignite Flare-Ups
Things around us can also trigger eczema. Dust mites, pollen, and strong soaps are common causes. Weather changes or pollutants can make symptoms worse. Knowing these triggers helps people manage their eczema effectively.
Eczema Flare-Ups: Understanding the Triggers
Eczema flare-ups can reduce the quality of life significantly. Knowing what triggers flare-ups is key to managing them. By recognizing both environmental and personal triggers, you can actively reduce flare-ups.
Common Environmental and Irritant Triggers
Environmental factors often cause irritation and flare-ups. Some common irritants include:
- Harsh soaps and detergents
- Extreme weather conditions, like cold or damp environments
- Airborne particles such as dust, smoke, and pet dander
- Fabrics that are irritating, like wool and polyester
- Certain food allergens and contact allergens
People in jobs like hairstyling or mechanics may notice work materials worsening their eczema. Taking steps to control your environment is key to reducing eczema triggers.
Stress and its Role in Eczema Flare-Ups
Studies show stress significantly affects eczema. It can worsen symptoms and increase flare-ups. Stress leads to inflammation in the body, which can worsen skin conditions. Thus, managing stress is crucial for those with eczema. Ways to manage stress include:
- Therapeutic approaches such as counseling or mindfulness
- Regular physical activity to relieve tension
- Engaging in relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation
- Building a supportive social circle
It’s important to understand both environmental triggers and stress’s impact on skin. This knowledge helps in making a plan to lessen flare-ups and their intensity.

Diagnosis and Treatment Methods
A dermatologist must look at a patient’s skin closely to diagnose eczema. They check the skin and symptoms. Sometimes, allergy tests help find the triggers of eczema. Knowing what you have early and accurately is key to treating it right.
How Dermatologists Diagnose Eczema
Dermatologists have many ways to confirm if someone has eczema. They look at the patient’s medical history and examine them closely. Things like itchiness, redness, and eczema bumps are important signs. By seeing a dermatologist often, treatment can change as the patient’s needs do.
Topical Steroids and Their Usage
Topical steroids are very important for treating atopic dermatitis. They lessen inflammation and the itch of eczema. Patients must use them as their doctor says to avoid side effects like thinning skin. These steroids help a lot right away and also work to prevent more flare-ups. Keep the skin moisturized and see your dermatologist often to check if the treatment is working. For more detailed info on eczema, check out this resource on eczema diagnosis and treatment.
| Medication | Type | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Topical Steroids | Corticosteroid | Reduces inflammation and itching |
| Pimecrolimus Cream | Calcineurin Inhibitor | Controls moderate to severe eczema |
| Dupilumab (Dupixent) | Systemic | Treats moderate to severe eczema |
| Light Therapy | Phototherapy | Reduces symptoms using UV light |
| Emollients | Moisturizer | Prevents and manages flare-ups |
Itch Relief Strategies for Eczema Bumps
Living with eczema bumps means seeking effective itch relief. This condition doesn’t just cause discomfort. It can also spark anxiety and mess with sleep. Thankfully, combining natural remedies and good skincare can ease the itch.
Top Natural Remedies for Soothing Itchiness
There are many natural remedies for itchy eczema skin. Let’s look at some popular options:
- Oatmeal baths calm inflamed skin with their anti-inflammatory powers.
- Coconut oil moisturizes and cuts down inflammation.
- Aloe vera cools, soothes instantly, and helps skin heal.
- Cold compresses numb the skin, curbing the scratching urge.
Using these treatments regularly improves skin health. It’s good to mix home remedies and store-bought products for the best result.
Importance of Moisturizing Cream
Moisturizing cream is a must for controlling eczema itch. A thick cream keeps moisture in, stopping the dryness that leads to more flare-ups. It works best right after a shower to lock in moisture.
| Feature | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Sunflower seed oil | Makes skin soft and is affordable. |
| Coconut oil | Feeds skin and lowers inflammation. |
| Hydrocortisone cream | Stops itch from getting worse if used early. |
Choosing these options can make a big difference in itch relief for eczema sufferers. It improves life quality and skin health.
Medication Options for Eczema Management
Handling eczema well often means using more than one treatment type. This can include creams for the skin and, sometimes, pills. The first treatments doctors usually suggest are creams or ointments. Corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors are top choices. They’re great at soothing the skin, reducing swelling, and making you less itchy and red.
Different strengths of these medicines let doctors find the right fit for each person. This way, the treatment matches how severe the eczema is.
Topical Treatments and Their Effectiveness
There are many kinds of corticosteroid creams. Some you can buy without a prescription. Others are stronger and need a doctor’s note. These creams can make the skin much better when used right. Also, moisturizers that fix the skin’s barrier help a lot. They keep the skin moist, stop it from drying out, and reduce redness and irritation.
Oral Medications and When They Are Needed
When creams don’t work, doctors might suggest pills or shots. These stronger treatments include immunomodulators. They’re for tougher cases of eczema. They cut down on itching and help the skin heal. If these don’t work, biologic injections might be the next step. It’s key for patients to work closely with their doctors. Together, they can come up with a plan that really makes a difference.
To learn more about eczema treatments, check out this resource.