More than 31 million Americans deal with eczema in its many shapes. Known as atopic dermatitis, this condition can really affect people’s lives. It shows up as itchy, inflamed rashes anywhere on the body. Eczema symptoms are different for everyone. That’s why knowing what eczema looks like is key to managing it early.
We created this guide to highlight eczema’s signs and features. With over 9.6 million children and 16.5 million adults in the U.S. having atopic dermatitis, understanding this skin issue is crucial. We’ll cover the various eczema rash types and share tips on managing this skin problem.
Key Takeaways
- Over 31 million Americans suffer from some form of eczema.
- Recognizing the signs of eczema can aid in early intervention and treatment.
- Eczema symptoms can appear anywhere on the body and vary by age.
- Atopic dermatitis is particularly common in young children but can persist into adulthood.
- Identifying triggers is crucial for effective management of eczema symptoms.
- Proper skin care routines can significantly help in preventing eczema flare-ups.
Understanding Eczema
Eczema is known by its eczema definition as a group of skin issues causing dry, itchy, and red skin. It’s often tied to atopic dermatitis and can appear in childhood or adulthood. Knowing the eczema causes helps in dealing with it.
Around 31.6 million people in the U.S. are living with eczema, with kids being most affected. Up to 20% of them face this, starting as babies. It hurts their life quality.
Children with eczema deal with red, itchy skin that can appear on different body parts as they grow. This condition can make kids extremely uncomfortable.
Managing eczema means keeping up with care. Seeing doctors especially when the season changes or symptoms worsen is key. Custom treatments might include special creams and antihistamines for better sleep.
Things like pet hair, dust mites, and pollen can make eczema worse. Skin infections also pose a threat, sometimes requiring antibiotics. But there are ways to fight skin bacteria and lower infection chances. Knowing what worsens eczema and finding the right help make a big difference.
What Does Eczema Look Like
Eczema comes in many forms, each with its own look. It’s important to know these signs for the right care. An eczema rash can change a lot, making it hard to spot. Recognizing its common traits helps catch it early for prompt help.
General Characteristics of Eczema Rash
Eczema often shows as red, dry, and cracked skin with an intense itch. Those with eczema might also find:
- Raised bumps that can ooze or weep when scratched.
- Thickened patches of skin that look like leather, from too much scratching.
- Color changes in the skin, turning darker or lighter, based on the body’s reaction.
Eczema can look different depending on your skin color. Knowing the specific signs helps in fully understanding the condition.
Variations Based on Skin Tone
Your skin tone can change how an eczema rash looks. For those with darker skin, rashes might be purple, brown, or gray. Lighter skin may show rashes as pink or red. Recognizing these differences is key to better managing eczema. Check out this guide for more on eczema’s impact on various skin types.
Signs of Eczema Symptoms
Eczema symptoms show up in many ways. It’s key to know these signs early. Different ages experience eczema differently. This knowledge helps in tackling the condition effectively.
Common Symptoms Experienced
Those with eczema might see a range of signs. These often include:
- Dry, cracked skin
- Intense itchiness
- Rashes appearing as small raised bumps
- Oozing and crusting in severe cases
- Thickened skin due to prolonged scratching
- Darkening of the skin around the eyes
There are many eczema symptoms. Knowing them helps treat kids and adults better.
How Symptoms May Vary by Age
Eczema shows differently at various ages. In babies, it’s mostly on the face and scalp, looking like oozing rashes. Older kids often get dry, scaly spots on elbows, knees, and neck.
Adults’ eczema might turn into hard, tough skin. It’s commonly on the hands, feet, or face. Watching eczema closely and caring for skin at all ages is crucial.
| Age Group | Common Symptoms | Typical Locations |
|---|---|---|
| Infants | Oozing, crusting | Face, scalp |
| Children | Dry patches, itchiness | Elbows, knees, neck |
| Adults | Thickened skin, severe itch | Hands, feet, face |
Types of Eczema
Eczema comes in many forms, each unique in characteristics and triggers. Knowing about these helps in diagnosis and treatment. Here, we look into the two most common kinds and some others.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is very common. It often affects people with family allergies, asthma, or hay fever. This eczema mainly starts in childhood and comes with itchy, red patches.
Things like skin barrier issues are a big cause.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is when skin reacts badly to certain substances. There are two types: irritant, caused by harsh substances, and allergic, caused by an allergy. Avoiding these substances can help symptoms get better within weeks.
Other Types of Eczema
Besides atopic and contact dermatitis, there are more kinds:
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis: Usually affects hands and feet, often in people who had atopic or contact dermatitis before.
- Nummular dermatitis: Seen more in middle-aged men but can occur in teenage women. Triggers can be skin injuries and it lasts a long time.
- Neurodermatitis: This type pops up in itchy areas like the neck, scalp, and wrists.
- Seborrheic dermatitis: Known for flaky skin, usually due to too much yeast.
- Stasis dermatitis: Mostly on the lower legs, related to bad blood flow. Can cause brown skin stains.
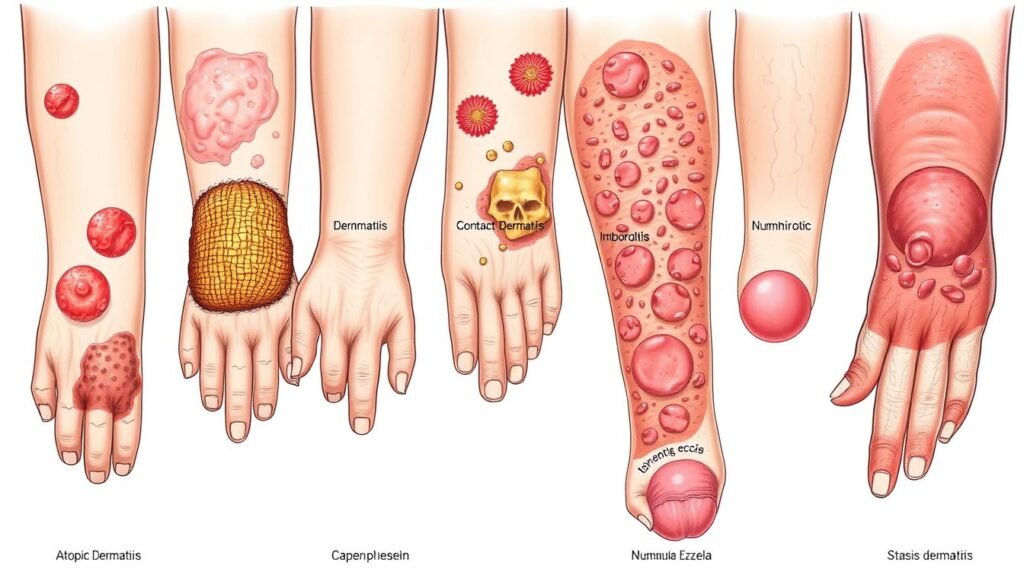
Knowing different eczema types helps find the right treatment for each one.
Eczema Causes and Triggers
Eczema comes from various factors that make it worse for some people. Genes play a big role in who might get this skin issue. If your family has had problems like asthma, hay fever, or allergies, you’re more likely to get eczema. Kids are especially at risk, with about 15% showing symptoms by the time they are 1 to 5 years old.
Identifying Common Triggers
Knowing what triggers eczema helps control it better. Some common triggers are:
- Harsh soaps and detergents
- Pollen and pet dander
- Changes in climate or temperature
- Food allergies
- Stress and hormonal fluctuations
Staying away from these triggers can really help cut down on eczema flare-ups. It’s key to remember that 33 to 63% of kids with bad eczema also react to certain foods. Knowing this link can help in finding ways to prevent and treat it.
Genetic and Environmental Factors
Genetics and environment together shape each person’s eczema. Stress, extreme weather, or dry air can make symptoms worse. What’s more, about 80% of kids with eczema might get asthma or allergic rhinitis as they grow. This insight helps in coming up with better ways to manage eczema in children.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Family history of atopic diseases increases susceptibility. |
| Environmental Triggers | Harsh soaps, pollen, pet dander, and extreme weather changes. |
| Food Allergies | Significant percentage of children with eczema also have food allergies. |
| Stress | Can aggravate symptoms and lead to flare-ups. |
What Eczema Flare-Ups Involve
Eczema flare-ups cause more severe symptoms. These include intense itching, redness, and swelling. Understanding the cycle of eczema is key to handling flare-ups well. Knowing what causes flare-ups helps people deal with their skin condition better.
Understanding the Flare-Up Cycle
The eczema cycle starts with irritation, then leads to inflammation. Flare-ups can be triggered by many things, like allergens and irritants. Things like hair dye, preservatives, and fragrances can cause reactions right away.
Irritants such as soaps, detergents, and strong cleansers can also lead to flare-ups. The length of a flare-up can vary, with some lasting weeks or more.
Managing Flare-Up Severity
To manage flare-ups well, combine several strategies. These help lower how often and how severe flare-ups are. Here are the key methods:
- Consistent Moisturizing: Use thick, fragrance-free moisturizers to keep skin hydrated and protected.
- Topical Treatments: Corticosteroids and calcineurin inhibitors reduce swelling and itching.
- Stress Management: Doing activities that lower stress helps improve overall health and might reduce flare-ups.
- Avoiding Triggers: Staying away from known allergens and irritants is key to avoiding flare-ups.
- Healthcare Consultation: If eczema gets worse or painful, it’s important to get advice and treatment from healthcare providers.

| Flare-Up Management Strategy | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| Moisturizing | Maintaining hydration and skin barrier. | High |
| Topical Treatments | Using corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors. | Medium to High |
| Stress Management | Adopting stress-relieving activities. | Medium |
| Avoiding Triggers | Steering clear of known allergens and irritants. | High |
| Consulting Healthcare Providers | Collaborating on personalized therapies. | High |
By learning about and managing eczema flare-ups well, people can greatly improve their comfort and skin health every day.
Eczema Treatment Options
Looking for the right eczema treatment can be tricky. It often mixes different methods to fit personal needs. People may try many options over time to control their symptoms. Treatments range from creams to natural fixes. Each has its own way to ease discomfort.
Topical Treatments and Medications
Topical creams are key for eczema care. Here are some common options:
- Hydrocortisone Cream: This low-strength steroid helps lessen redness and swelling.
- Calcineurin Inhibitors: Ointments like tacrolimus and pimecrolimus work for those older than 2. They help manage immune reactions.
- PDE4 Inhibitors: Eucrisa® blocks certain body reactions, reducing symptoms.
- JAK Inhibitors: Ruxolitinib (Opzelura) is a cream that directly fights inflammation.
For tougher atopic dermatitis, shots like dupilumab (Dupixent) and tralokinumab (Adbry) are safe and work well. If creams don’t help, phototherapy might. It uses UV light carefully to help.
Home Remedies for Eczema Relief
Home methods can also ease eczema. Simple steps can make skin moist and less irritated:
- Moisturization: Moisturizing twice a day helps keep skin soft, fighting dryness.
- Oatmeal Baths: Colloidal oatmeal baths calm itchy skin.
- Diluted Bleach Baths: The American Academy of Dermatology suggests this to cut down on itch and flare-ups.
- Oral Antihistamines: Medicines like cetirizine reduce itching and aid sleep.
Using these home tips can boost eczema care. But, if symptoms stay bad, see a doctor to get the best plan. Custom treatments can really help with this lasting issue.
Preventing Eczema Flare-Ups
Knowing how to stop eczema flare-ups is key for those with the condition. Keeping the skin moist with a regular creaming routine helps avoid dry, itchy patches. It’s also important to pick the right products. Knowing what triggers your eczema and avoiding those things is essential. This helps you keep flare-ups under control.
Establishing a Regular Moisturizing Routine
Having a good moisturizing routine is crucial for fighting eczema. Use thick, fragrance-free creams often to keep the skin moist. Apply them after showering and any time your skin feels dry. Choose creams that don’t have stuff in them that can make eczema worse. Moisturizing not only keeps the skin soft but also protects it from things that can irritate it.
Avoiding Known Triggers
Avoiding things that set off your eczema is a big part of controlling it. People have different triggers, but they often include:
- Sweat from exercise
- Irritating fabrics like wool
- Pet hair
- Very hot or cold weather
- Strong soaps and cleaners
Staying away from these irritants is important to cut down on flare-ups. Things like dust, smoke, and other allergens can also make eczema worse, so keep your place clean. Managing stress well can help too, as stress can sometimes cause eczema to flare. Talking to a doctor about your triggers can help make a plan that works for you.

Eczema in Children and Infants
Eczema is a skin issue common in kids and often starts in babies. Parents need to know its symptoms and how to help their kids. Knowing early signs is key to helping infants right away.
Symptoms in Infants
Infant eczema usually shows up in the first few months as crusty, flaky spots. You’ll see it on their cheeks and the joints of arms and legs. Eczema looks different on varying skin tones. For light-skinned babies, it appears red. In darker-skinned babies, it might look purple, brown, or gray. Understanding these differences is important for the right care.
Managing Eczema in Young Children
Dealing with eczema in young kids requires a few steps. Parents should use lukewarm baths and mild soaps. It’s best to dress them in soft cotton clothes to keep skin comfy. Daily use of ceramide-rich creams moisturizes skin and helps keep it healthy. Watch out for common triggers like allergens and dry air to keep eczema at bay.
Sometimes, hydrocortisone creams available at stores can reduce itching and swelling. If the issue doesn’t get better after a week, or if the skin looks infected, see a doctor. Getting help early makes managing eczema easier and can make a big difference in a child’s life.
Conclusion
Knowing how to spot eczema is key to handling it well. In the U.S., about 31.6 million people have it. That’s nearly 10% of folks dealing with different types of eczema, including the common atopic dermatitis. Spotting the early signs and symptoms is vital. These can change depending on age and skin color.
Children are often affected, with 1 in 4 getting atopic dermatitis by age 5. It’s important for parents to know what to look for. This knowledge helps in starting the right treatment early on.
Managing eczema isn’t just about medical treatments like creams and biologics. Home care, which includes baths and moisturizing, also plays a big role. Staying away from triggers, like some foods or fabrics, helps improve life for those with eczema. Thanks to ongoing research, there’s hope for even better ways to manage eczema, as the CDC points out.
Wrapping up, dealing with eczema means being informed and active. Learning about this condition lets people take charge of their skin health. This leads to a better life, dealing with eczema. There are many ways to manage eczema, from seeing a skin doctor to trying home remedies. With the right info and tools, anyone can navigate their way through eczema care.