Did you know irritant contact dermatitis makes up 80% of contact dermatitis cases? It’s a common condition that brings a lot of discomfort. It happens from simple things like touching everyday irritants or allergens. Contact dermatitis shows up as an itchy rash from touching stuff like makeup, scents, or some plants.
Though it can’t spread from person to person, the itchiness can be really bothersome. Symptoms usually appear days after touching the irritant. The good news is, with the right care, it gets better in 2 to 4 weeks.
Let’s dive deeper into contact dermatitis, covering what causes it, symptoms, and how to manage it well. How what you eat affects it is also key; learn more in this guide on diet and nutrition. It has helpful info for those dealing with this issue.
Key Takeaways
- Contact dermatitis is characterized by an itchy rash caused by skin contact with irritants or allergens.
- Common symptoms include dry, red, and crusting skin or lesions that can become severe.
- Identifying and avoiding known triggers is crucial for effective management.
- Irritant contact dermatitis is the most prevalent type, particularly among professionals handling chemicals.
- Treatment typically involves over-the-counter remedies or prescription medications from healthcare professionals.
- Understanding the difference between irritant and allergic contact dermatitis is vital for proper diagnosis.
Understanding Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis shows up as an inflamed skin reaction after touching certain things. It makes skin itchy, blistered, or dry. It splits into two kinds: irritant and allergic contact dermatitis. Knowing about it helps manage and prevent it.
Irritant contact dermatitis comes from skin damage by things like soaps and solvents. Cutting fluids are major irritants too. A survey found about 1,700 workers get occupational contact dermatitis per 100,000 in fields like manufacturing and health services.
Allergic contact dermatitis is less common but happens when the body reacts to things like nickel or urushiol in poison ivy. About 70% of people may react to urushiol. Interestingly, 64% of allergic dermatitis cases affect the hands.
To better understand contact dermatitis and treatments, looking into emollients and steroids is key. Avoiding irritants or allergens is crucial for healthy skin. Check out more information here.
What is Contact Dermatitis?
Contact dermatitis is when your skin gets inflamed after touching certain things. This can happen with irritants or allergens. There are two main types: irritant contact dermatitis and allergic contact dermatitis. It’s important to know the difference for proper treatment.
Definition and Overview
Contact dermatitis makes your skin rashy after touching allergens. Things like nickel, fragrances, and some medicines can cause it. If you already have skin issues, like eczema, irritant contact dermatitis could be a bigger problem for you. Acids, strong soaps, and poison ivy are usual suspects.
A look into contact dermatitis shows allergic responses involve the immune system. But, irritants don’t need the immune system to cause trouble. Symptoms can show up quickly or take days. Depending on what caused it, the rash could stick around for weeks or even longer.
Non-contagious Nature of the Condition
Non-contagious contact dermatitis can’t spread from person to person. It’s due to personal sensitivity to certain substances. Understanding this can reduce worry about the rash in social settings. It lets those affected seek help without fear of spreading it.
Common Symptoms of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis has symptoms that really affect your life. Knowing these symptoms helps manage and treat them. Each person’s skin reacts differently to this condition.
Itchy Rash and Skin Discomfort
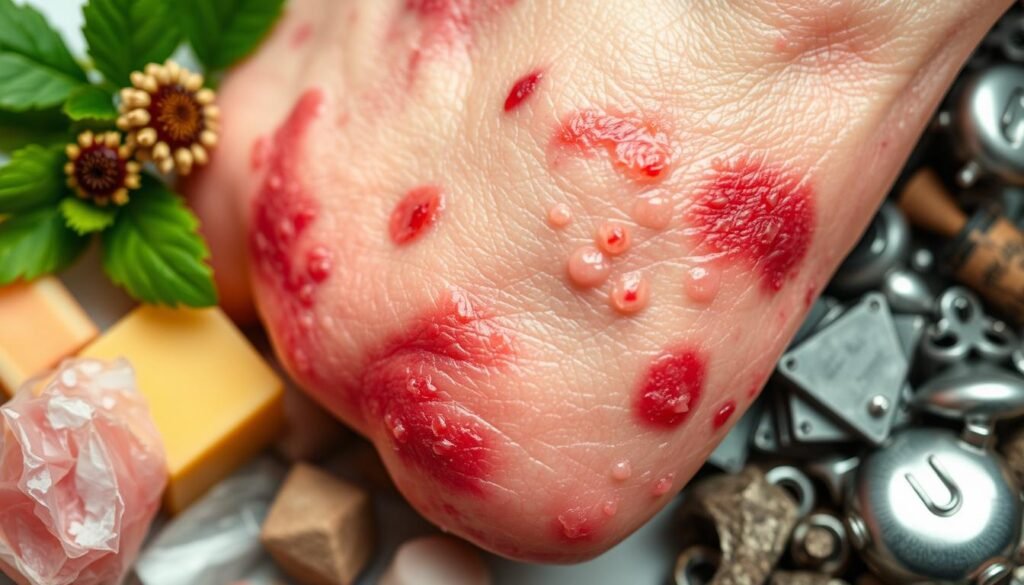
The main signs of Contact Dermatitis Symptoms are an itchy rash. This can cause a lot of discomfort. The rash might look red, swell, and hurt. Dry, flaky skin is common too. Sometimes, bumps or blisters with clear fluid appear. These symptoms usually start a few hours to ten days after touching irritants or allergens.
Variations in Symptoms on Different Skin Types
Different skin types show Contact Dermatitis Variations differently. Darker skin might get dark spots. Lighter skin often shows redness and dryness. It’s key to know how your skin reacts, mainly when picking treatment plans. About 8% of adults get contact allergies, and women get them more than men.
Possible Complications from Scratching
Scratching an itchy rash feels good but can cause complications of contact dermatitis. It can make irritation worse and raise the chance of infection. Oozing skin can attract bacteria, leading to more issues. Keep the area clean and seek help if needed. For more info, check out this page.
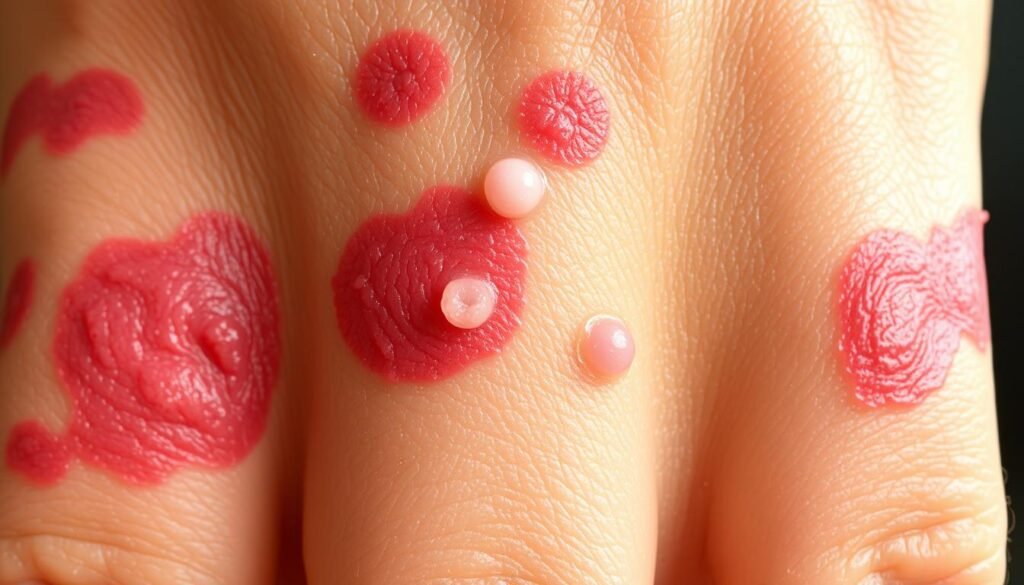

Causes of Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis happens when skin reacts to irritants or allergens. Many things can cause it. Knowing what they are helps in treating and preventing it. There are two types of contact dermatitis: irritant and allergic. Each has different triggers that matter for treatment and prevention.
Types of Irritants and Allergens
Irritants and allergens can cause contact dermatitis. Some common irritants include:
- Soaps and detergents
- Solvents and bleach
- Certain plants, notably poison ivy
Allergens that might trigger reactions include:
- Nickel, chrome, and mercury
- Fragrances and preservatives in skincare products
- Paraphenylenediamine found in permanent hair dyes
- Neomycin in certain topical medications
These substances can start an immune response or harm the skin directly. This causes inflammation and discomfort.
Difference Between Irritant and Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Irritant and allergic contact dermatitis have different causes. Irritant contact dermatitis makes up about 80% of cases. It happens when irritants damage the skin. Symptoms include redness, swelling, blisters, and itching. Anyone can get it, from babies to the elderly, especially those with atopic tendencies.
Allergic contact dermatitis is different. It’s when the immune system reacts to certain allergens. Both children and adults can get it, but adults see it more. Poison ivy is a common cause, affecting up to 70% of adults in the U.S. Knowing the difference is key for the right treatment.

Identifying Triggers: Contact Dermatitis Management
Understanding triggers is key in managing Contact Dermatitis effectively. Knowing everyday irritants can really help lower the chances of skin reactions. Things like household cleaners, skincare products, and certain fabrics can irritate the skin.
Common Irritants in Everyday Life
Everyday life is full of substances that could cause contact dermatitis. It’s critical to know what these triggers are. Some common ones include:
- Soaps and detergents
- Acids and bases
- Solvents used in cleaning
- Saliva, urine, and stool
- {{Poison ivy}}
- Fragrances and cosmetics
- Medications and dyes
- Scratchy fabrics
Identifying Allergens Through Testing
To find out what you’re allergic to, Contact Dermatitis Testing is essential. The patch test is a common way to do this. It means putting small amounts of different things on your skin. Then doctors watch for a reaction after 48 and again at 72 to 96 hours. Knowing your allergens helps you avoid them, reducing future skin issues.
If you react to things like nickel or rubber gloves, learning what to do to prevent it is helpful. For irritant contact dermatitis, staying away from the cause is key. This is especially true for those who work with chemicals, like healthcare workers and cleaners.
| Type of Contact Dermatitis | Common Triggers | Prevalence |
|---|---|---|
| Irritant Contact Dermatitis | Soaps, detergents, bleach, solvents | 80% of cases |
| Allergic Contact Dermatitis | Cosmetics, poison ivy, nickel | 15% to 20% of individuals |
Successfully managing contact dermatitis means knowing common irritants and getting tested to identify allergens. This helps people lead healthier lives without skin irritation.
How to Diagnose Contact Dermatitis
Finding out if you have contact dermatitis requires attention to detail. You must consult experts in healthcare. They work to spot allergens and irritants that cause this skin issue. A detailed assessment includes looking into your health history and checking your skin. It also involves talking about any past contact with likely triggers.
Consultations with Healthcare Providers
People needing help with contact dermatitis should see dermatology experts. These doctors look at your symptoms and suggest ways to figure out what you have. Talking about any allergies and what you’re exposed to every day helps. This makes finding out if you have Contact Dermatitis more precise. The provider might ask about places you work or any known allergies. This helps them understand what kind of dermatitis you might have.
Patch Testing Procedures Explained
Patch Testing is key for spotting allergic forms of contact dermatitis. In this test, small patches with different allergens are placed on your skin. They stay there for 48 hours to see if there’s a reaction. This way, doctors can tell what’s causing your allergy, such as nickel or certain chemicals. After the test, they can advise you on what to avoid. This helps in planning how to care for your skin better.
| Test Method | Purpose | Reaction Evaluation Time |
|---|---|---|
| Patch Testing | Identify allergens triggering reactions | 48 hours |
| Skin Prick Test | Determine immediate hypersensitivity | 15–20 minutes |
| Serum IgE Testing | Measure allergic reactions within the bloodstream | 1–2 weeks |
Knowing how to diagnose contact dermatitis allows for better treatment. It’s important for patients and doctors to work together. This teamwork leads to better care for your skin.
For more on Contact Dermatitis diagnosis, see this link.
Contact Dermatitis Treatments
Managing contact dermatitis usually involves both Over-the-Counter and prescription treatments. These are chosen based on how severe the condition is and what’s causing it. The main goal is to ease discomfort and help the skin heal.
Over-the-Counter Remedies
If you have a mild or moderate case, there are several Over-the-Counter remedies. They help soothe your skin. You might find:
- Hydrocortisone Cream: This cream reduces inflammation and eases itchy skin.
- Anti-itch Lotions: Look for products with calamine or colloidal oatmeal for itch relief.
- Moisturizers: Using hypoallergenic moisturizers regularly can protect your skin and stop irritation.
You can easily find these treatments at most pharmacies. This makes it simple for people with contact dermatitis to get relief.
Prescription Medications for Severe Cases
For severe contact dermatitis, Over-the-Counter products might not be enough. In these cases, doctors may prescribe stronger treatments. You could be given:
- Topical Steroids: These are more powerful than what you find Over-the-Counter, reducing inflammation faster.
- Oral Corticosteroids: For extreme, widespread rashes, oral steroids might be used to reduce inflammation in the body.
If symptoms worsen or reactions are severe, it’s crucial to seek medical help quickly. Prompt treatment ensures proper handling of contact dermatitis.
| Treatment Type | Indications | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Over-the-Counter | Mild to moderate symptoms | Hydrocortisone Cream, Calamine Lotion, Moisturizers |
| Prescription | Severe Contact Dermatitis | Topical Steroids, Oral Corticosteroids |
Contact Dermatitis Prevention Strategies
To prevent contact dermatitis, it’s important to know and avoid triggers. Keeping track of reactions helps identify what to steer clear of. This makes it easier to follow Contact Dermatitis Prevention methods. It means less discomfort and irritation for you.
Identifying and Avoiding Known Triggers
Things like nickel, certain plants, and chemicals often cause allergic contact dermatitis. For irritant contact dermatitis, common items like soaps and rubber gloves are culprits. By actively avoiding these items, you can cut down on exposure. It’s also good to check your surroundings regularly. This helps avoid situations that may lead to a reaction.
Protective Measures and Skincare Routines
A good skincare routine is key to protecting your skin. Using moisturizers regularly keeps your skin barrier strong. Wearing protective clothing helps, too, especially when around potential irritants. Barrier creams are also effective in guarding against contact dermatitis. Learning and keeping up with these skincare steps is vital. It prevents symptoms and complications from contact dermatitis.